Linux For Dummies
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-sourced OS, was created by Linus Torvalds as a hobby and written 98% of the code in C Programming Language.
Linux source code is freely available here
The structure of the linux File System
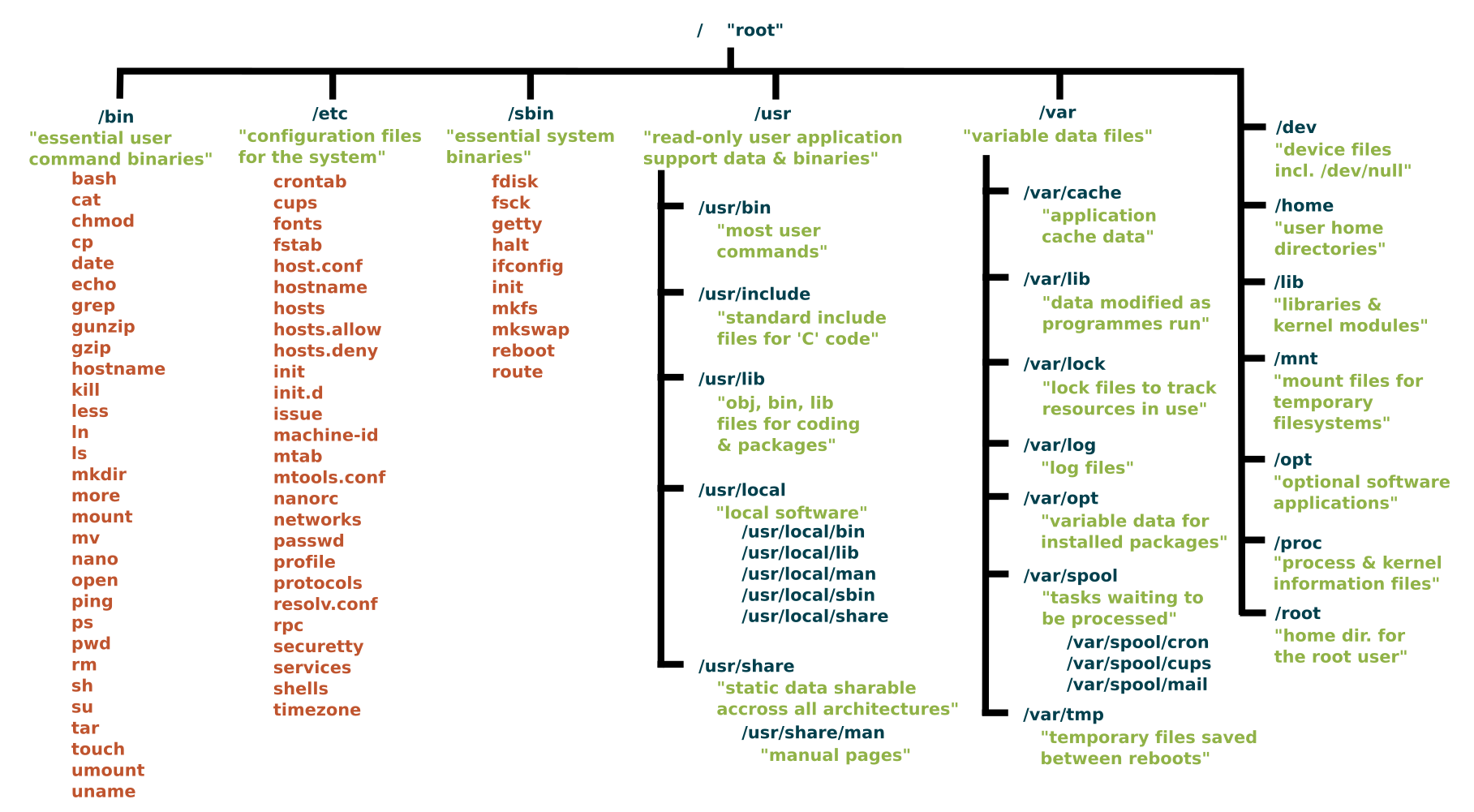
Will discuss about key things in Linux from the above image further in our discussion.
Why Linux?
There are many reasons for Linux to be extremely popular, will try to list key factors here:
- Linux has less security flaws
- As Linux is Open-Source code, huge number of developers will review the code constantly
- Linux has password authentication, file system discretionary access control, and security auditing, these 3 fundamental security features are essential
- Linux is Free OS
- Linux has no license cost to use it unlike other OS like Windows
- Performance
- Linux doesn’t have bloat UI features which makes it light weight
- Linux can run on almost any architecture (
x86,ARM,RISC-V.. etc) - Linux has organized file system hence it is easy to perform file operations quickly
- Task Automation
- Because of default shell (
bash,zsh,sh.. etc) support in Linux, users can automate most of the regular stuff efficiently on Linux
- Because of default shell (
How to Install Linux
There are many varients of Linux is available for public. why?
- Why there are so many cars? Because there are several vehicle manufacturers using the same engine and each of them has different types and for different purposes. Since the
Linux engineis free to use and modify, anyone can use it to build a vehicle on top of it.
For Servers: CentOS 8 (RHEL without License) is most widely used across data centers.
Getting Started with Linux
Large portions of Linux functionality are achieved using the terminal, Bash (Bourne Again SHell) is a common default shell among many Linux distributions. To know which Shell is default in your system:
$ echo $SHELL # To know default Shell
$ echo $0 # To know default Shell
$ chsh -l # To know all available Shells in the machine
$ cat /etc/shells # To know all available Shells in the machine
$ chsh -s /usr/bin/sh # To chnage the Shell for user, this will require reboot
File Management Commands
$ pwd # prints current working dir full path
$ cd - # To goto last working directory
$ cd .. # To goto parent directory
$ cd # To goto home directory
$ ls # list all files in pwd
$ ls -a # list all files in pwd including hidden files ex: .dir/
$ tree # represents file system in tree format
$ cp -r src/ dst/ # To copy recursivly all files in src/ to dst/
$ cp file1 file2 # To copy file contents from file1 to file2
$ mv src/ dst/ # To move all files in src/ to dst/ and rename src/ to dst/
$ mv file1 file2 # To rename file1 as file2
$ chmod <specification> file # Specifications = u user, g group, o other, + add permission, - remove, r read, w write,x execute
$ chmod 777 file # Give read, write and execute permissions to file
$ chown owner1 file # Change file owner to owner1
$ chgrp grp_owner file # Change group permissions to grp_owner
Create New User
$ useradd mohan # Creates username
$ groupmod mohan # Creates Group name
$ passwd mohan # Asks for user input to set password
$ mkdir /home/mohan -p # Creates user space under home
$ chown -R mohan:mohan /home/mohan # Setup group policies
$ usermod -d /home/mohan -m mohan # Modifies user login
$ sudo chsh -s /bin/bash mohan # Change default shell to bin/bash
Note: To create new user, we need to have sudo permissions on the machine
Basic Linux Utilities
$ man cat # To read manual of cat tool
$ help echo # This will display the info about the "echo" bash command
$ hostname # To dispaly hostname
$ passwd # To change the password
$ w # system status and list of users logging in that machine
$ last # who recently used the system
$ top # List all processes sorted by their current system resource usage
$ ps aux # List all the processes by all users on the current system
File Search Operations
$ find /var/www -name '*.css' # find all files ends with .css from /var/www dir
$ grep font /var/www/html/style.css # Print all lines containing the pattern font in the specified file
$ touch file # Create empty file
$ cat file # print all the contents of the file
$ head file # print first few lines of file
$ tail file # print last few lines of file
$ less file # View the content of a file with pager (one screenful at a time)