High Performance Computing For Dummies
What is HPC?
There is no single definition for High Performance Computing, HPC is a field dedicated to computers aimed at improving computing performance and perform complex calculations and uses clusters of servers that work in parallel to achieve the same.
Who needs HPC?
HPC solutions can be million times more powerful than the fastest laptop. This power allows enterprises to run large analytical computations, such as millions of scenarios that use up to terabytes (TBs) of data. For example, weather forecasting or risk management assessments. Organizations can also run design simulations before physically building items like chips or cars.
Various forms for HPC?
Organizations can choose different ways to design HPC systems.
Parallel Computing
In single server, parallel computing takes large workload and splits them into separate computational tasks that are carried out at the same time. In multiple servers, splitting same job into manageable parts, and distributing those parts to multiple servers or computers with all work performed in parallel.
Cluster Computing
Cluster computing is a type of parallel HPC system consisting of a collection of computers working together as an integrated resource. It includes scheduler, compute, and storage capabilities.
Grid Computing
Grid computing is a heterogeneous network whose devices have different hardware components and different OS connected in a grid.
High performance computers of interest to small and medium-sized businesses today are really clusters of computers.
What is Supercomputer then?
Supercomputers are monster machines that work on some of mankind’s biggest problems in science and engineering and they are only good for specialized problems. Supercomputing is also one form of HPC.
Fugaku: #1 supercomputer in the world with a computing speed of 442 petaflops, was used to simulate the spread of the coronavirus through droplet dispersion. It was also involved in forecasting concentrated downpours and other weather events.

HPC and Data Centers are same?
Both use the same basic components servers, networks, storage arrays but are optimized for different types of applications. Those within the data center are largely transaction oriented while HPC applications crunch numbers and high volumes of data. However, High performance computing (HPC) data center is a fast-growing segment, and several off-premises HPC data centers are developing, especially in European Nordics countries.
Cloud Computing and HPC?
With advancements in cloud technologies, HPC solutions have become more accessible and affordable to enterprises. Today, organizations can access a wider variety of HPC applications and dynamic resources with only a high-speed internet connection with cloud benefits, such as flexibility, efficiency, and strategic value.
What is a Server, Anyways?
- A dedicated computer, that provides services on behalf of client (desktop/laptop), so, it’s a powerful centralized machine where clients are connected over Internet or LAN.
- What kind of services does Server provides
- Website hosting
- Email hosting
- Database hosting, etc.,
- 1 Server can provide 1 or more services from above list based on the demand vs ability to serve.
- Servers are designed to handle large workloads whereas client machines are inferior to both hardware and software, because laptop/desktop operating systems are capable of handling limited number of concurrent connections.
- Servers need to be up and running 24/7 with little to no down time, if server goes down that will damage the business.
- Intel Xeon and AMD EPYC processors support multi-processing environment i.e., we can put more than 1 processor on a single motherboard.
- Intel Xeon and AMD EPYC processors will support larger amount of RAM, will have larger Cache and higher core count than client processors.
- Servers will also have hot swappable hard drives in a RAID configuration to avoid issues when the one hard drive fails, Server should also have redundant power supply to keep the server alive in case if one power supply fails.
- Server needs to use a server OS such as Linux, Windows Server. Server OS is designed to be robust and handle concurrent requests.
- Examples for processors used in Servers are AMD EPYC or Intel Xeon Processors, whereas for desktop/laptops Core i Series or AMD Ryzen Series.
Mother Borad of Comptute Server with 2 Processor
Storage Server with RAID Memory Configuration
Network Server
Server Rack

Server Room

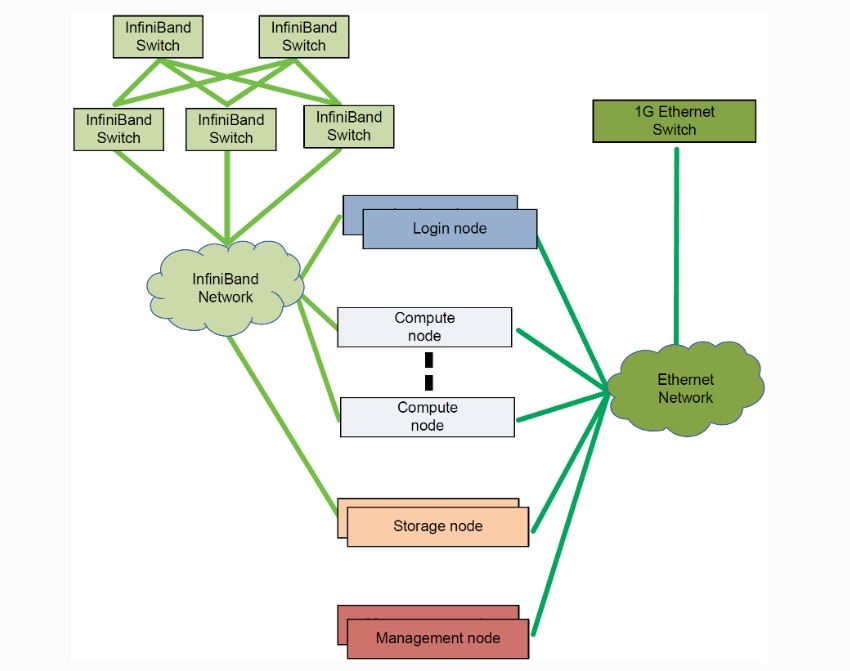
Anatomy of HPC Cluster
A typical HPC solution has 3 main components:
- Compute
- Network
- Storage
HPC solutions can be deployed on-premises, at the edge, or even in the cloud.
The point of having a high-performance cluster is so that the individual nodes can work together to solve a problem larger than any one computer can easily solve. And, just like people, the nodes need to be able to talk to one another to work meaningfully together. Of course, computers talk to each other over networks, and there are a variety of computer network (or Interconnect).
Depending on how the nodes are connected various topologies evolved, most popular topologies are:
Popular topologies are
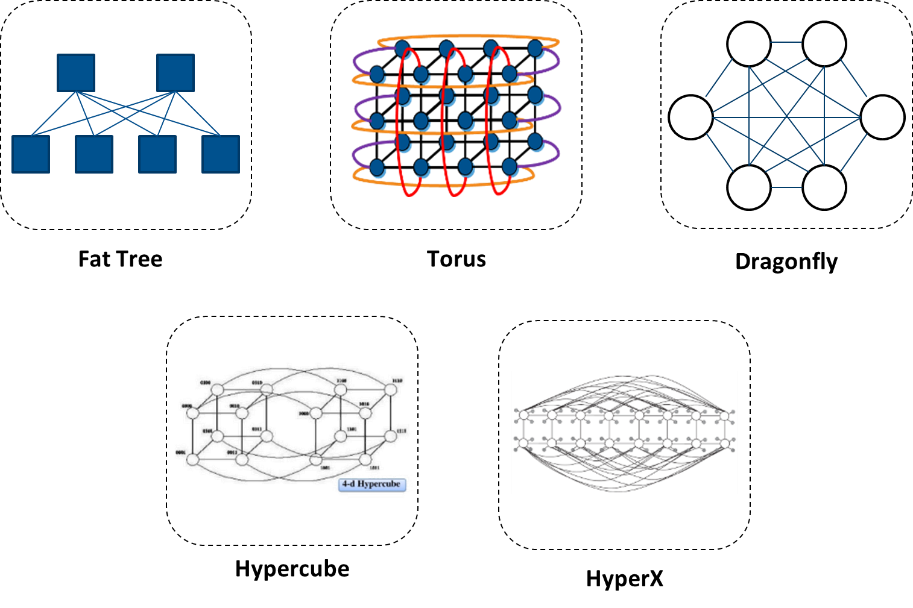
Fat-Tree is one of the most widely used topologies. It is a good option for a variety of applications as it provides low latency and enables a variety of throughput options – from non-blocking connectivity to oversubscriptions. Highly scalable dragonfly topology provides good performance for a variety of applications (or communication patterns), like Fat-Tree; specifically, it reduces network costs compared to other topologies, by reducing the number of long links.
Exmaple block diagram for Fat-Tree topology
Head node or login node
This node validates users and may set up specific software on the compute nodes.
Compute Nodes
These nodes perform the numerical computations and will probably contain the highest clock rates available and affordable with the maximum number of cores at the given clock rate. The persistent storage on these nodes may be minimal, while the DRAM memory will be high.
Storage Nodes or Storage System
An efficient HPC cluster will need to contain a high performance, parallel file system (PFS). A PFS allows for all nodes to communicate in parallel to the storage drives. HPC storage allows for the compute nodes to operate with minimal wait times.
Network Fabric
In HPC clusters, typically, an Infiniband or high performing Ethernet network switch will be used, due to the requirement of low latency and high bandwidth features.
Software
Software for an efficiently running of an HPC cluster needs to manage the massive amounts of I/O that are inherent to HPC applications. Reading and writing of data in parallel from the large numbers of CPUs to the storage system (whether internal or external to the servers) should be considered critical and not be ignored.
The core of any HPC cluster is the scheduler, used to keep track of available resources, allowing job requests to be efficiently assigned to various compute resources (CPU and GPU) via fast network.
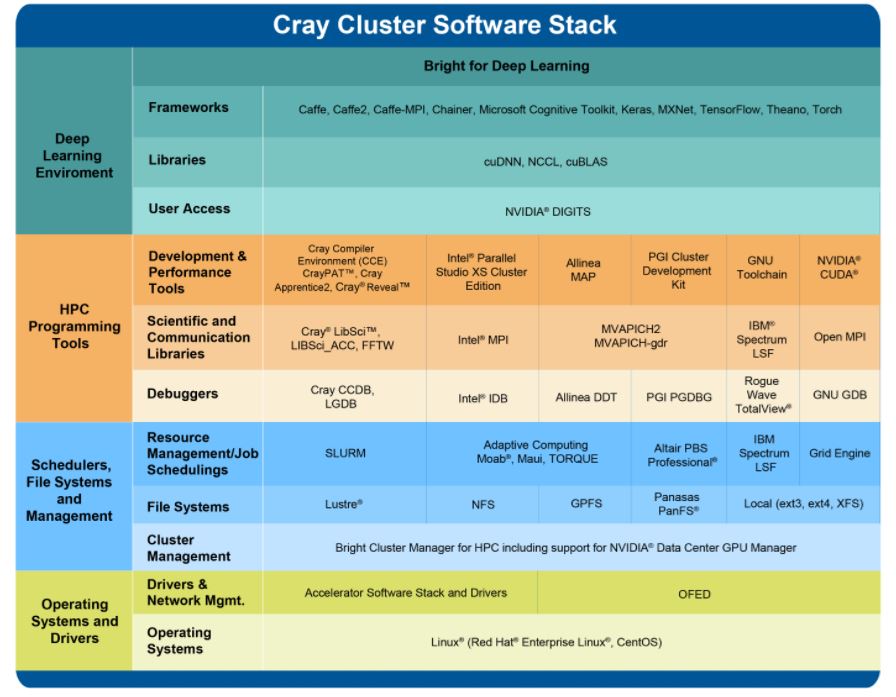
Open Source Tools for Cluster Management
- OpenHPC
- OpenHPC is a collaborative, community effort that initiated from a desire to aggregate a number of common ingredients required to deploy and manage High Performance Computing (HPC) Linux clusters including provisioning tools, resource management, I/O clients, development tools, and a variety of scientific libraries. Packages provided by OpenHPC have been pre-built with HPC integration in mind with a goal to provide re-usable building blocks for the HPC community.
- Link: https://openhpc.community/
HPC Applications
HPC is used in many real-life scenarios to solve complex problems in science, business, and engineering. Some academic institutions also use HPC systems. Some government agencies, particularly the military, rely on HPC for complex applications. As the demand for processing power and speed grows for real-world applications.
- Genomics: For DNA sequencing, lineage studies, and drug analysis
- Medicine: Drug research, vaccine production, therapy research
- Industrial sector: Simulations and models, e.g., artificial intelligence, machine learning, autonomous driving, or process optimization\
- Aerospace: Simulations on aerodynamics
- Finance: In the context of financial technology to perform risk analysis, fraud detection, business analysis, or financial modeling
- Entertainment: Special effects, animation, transfer of files
- Meteorology and climatology: Weather forecasting, climate models, disaster forecasts, and warnings
- Particle physics: Calculations and simulations of quantum mechanics/physics
- Quantum chemistry: Quantum chemical calculations